Research in our lab is dedicated to understanding the role of the Alzheimer's disease risk factor Apolipoprotein E (APOE) in cerebral metabolism. With a special focus on glia and their contributions to neurodegeneration, we employ a variety of transcriptomic and metabolomic approaches (from cells to mice to humans) in order to identify early-life changes in metabolism associated with APOE. Our lab's overarching goal is to discover new therapeutic targets that will allow us to reprogram metabolism in individuals at-risk for Alzheimer's disease in order to enhance cognitive resilience and to extend the brain’s health span.
FEATURED NEWS!
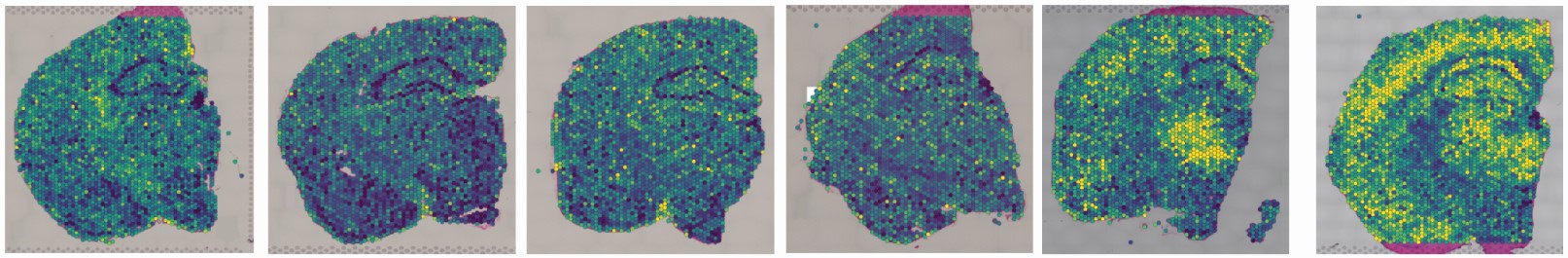
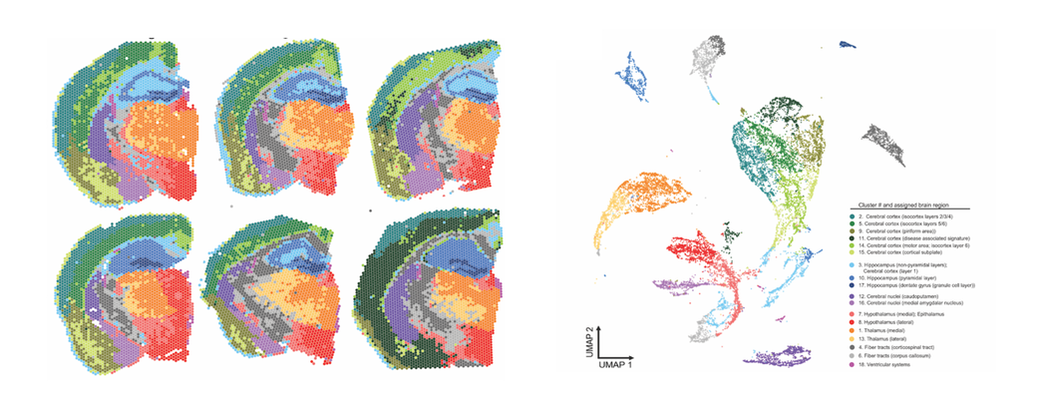
We just launched the Johnson & Morganti Lab interactive datasets exploring the role of APOE across aging, inflammation, and AD pathology. The following datasets are comprised of i) whole brain tissue (bulk) sequencing, ii) whole brain scRNAseq, iii) microglia only scRNAseq, and iv) spatial transcriptomics. Brains from female APOE3 and APOE4 mice were analyzed across the lifespan (3, 12 and 24 months of age), and in the presence of an inflammatory challenge (LPS) or AD pathology (amyloid overexpression). For details on methodology, please see Lee, Devanney et al., 2022.
Recent Move to New Lab Space!
We recently moved to the 1st floor of the Healthy Kentucky Research Building (HKRB). Photographs of the new lab space are below.
We recently moved to the 1st floor of the Healthy Kentucky Research Building (HKRB). Photographs of the new lab space are below.
Meet Our Team
We are constantly expanding our research team. Please contact us for more information!
We are constantly expanding our research team. Please contact us for more information!
Research
Ongoing Projects
|
APOE & the PPP
The central hypothesis of this project is that APOE influences neuronal function and survival through isoform-specific changes in glucose metabolism via the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). To test our hypothesis, we are employing a unique ‘omics approach to test a novel mechanism which potentially ties E4 to neuropathological changes in cerebral glucose metabolism, oxidative stress and neuronal survival. |
Mapping Metabolism in the Aging Brain
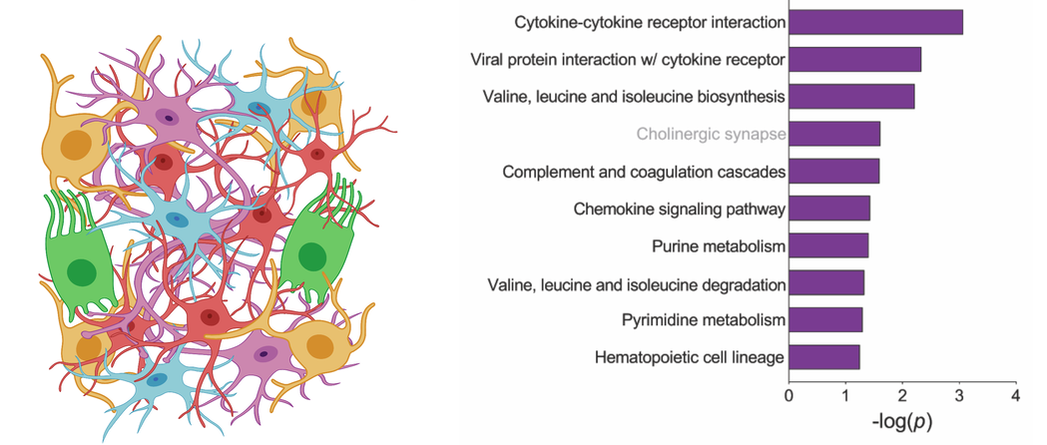
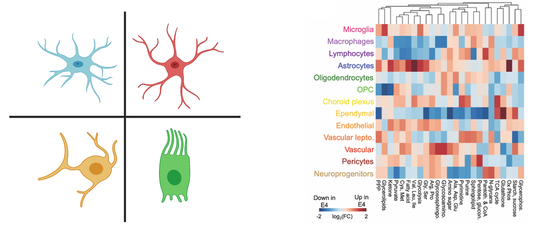
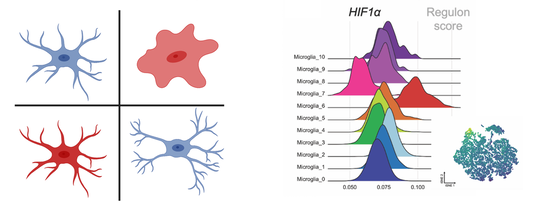
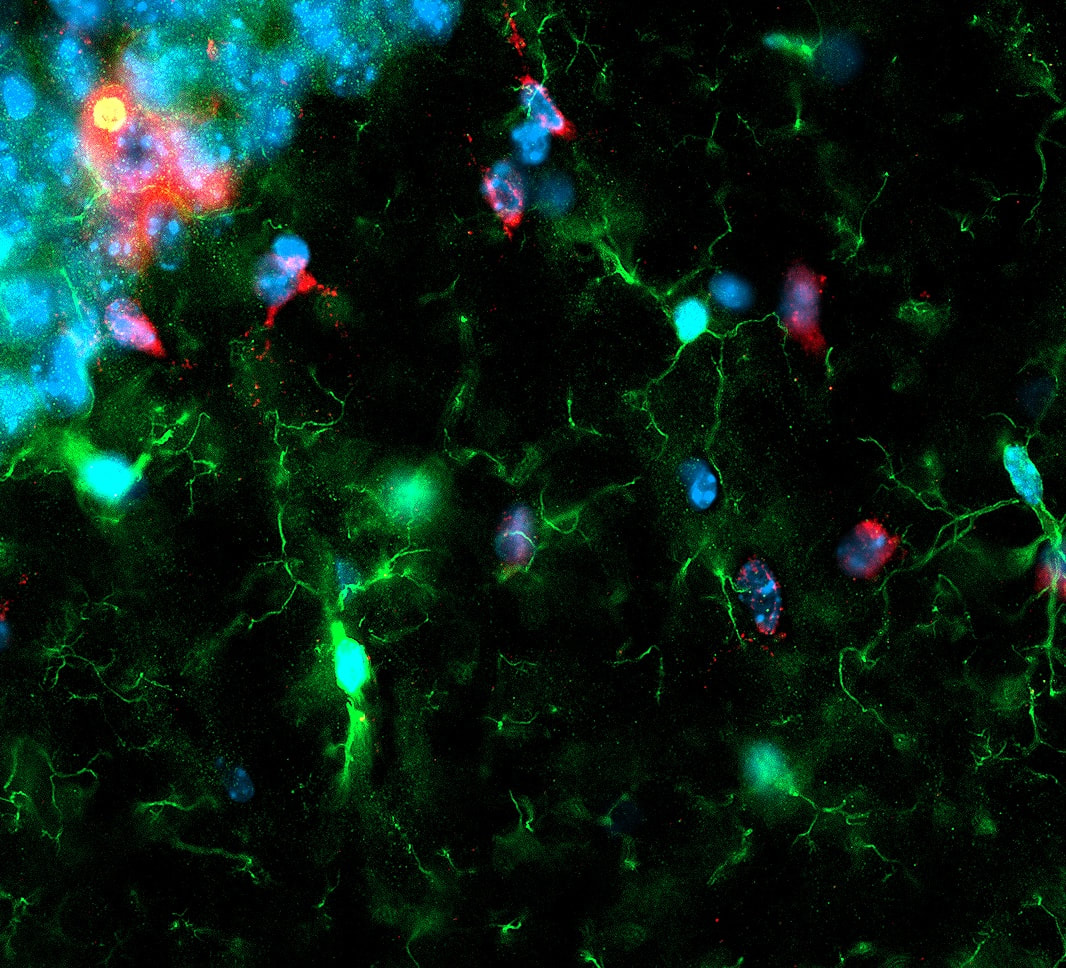
Cerebral metabolism is based on a complex interplay between multiple cell types. What types of changes do each of these cells undergo during aging and in disease? Does APOE play a role? To begin to try to answer these questions, we are using a combination of single cell and spatial transcriptomic approaches to map metabolic changes in the brain across multiple cell types and brain regions. [In collaboration with Morganti and Sun labs] |
Lipid Droplets, APOE, & AD
Interestingly, Dr. Alois Alzheimer's original findings in 1907 was that glial cells contained "adipose saccules." Many now think he was referring to lipid droplets. Does APOE have a role to play in modulating lipid droplet dynamics in the Alzheimer's (AD) brain? Our lab is attempting to answer that question using a combination of in vitro, in vivo and ex vivo approaches to probe the role of APOE in modulating lipid metabolism and lipid droplet biology. |
The APOE "Switch" Mouse:
A Novel Mouse Model Our novel transgenic model, the APOE “switch mouse” (4s2), uses the Cre-loxP system to allow for inducible APOE allele switching from APOE4 to APOE2. Our exciting preliminary studies leverage this new mouse as a promising model to assess the therapeutic potential of replacing APOE4 with APOE2 and to investigate how we can utilize ApoE2’s neuroprotective effects to mitigate ApoE4-associated AD pathologies. Ongoing studies aim to determine whether the cell-specific replacement of APOE4 with APOE2 will rescue E4-associated metabolic dysfunction, disease-associated gene signatures, and AD pathology. |